1. Introduction to DC/DC Converters in EVs
In modern electric vehicles (EVs), there are two primary battery systems:
* High-voltage lithium-ion battery for powering the traction motor.
* Low-voltage lead-acid battery for auxiliary systems like headlights, infotainment, ECU, and safety electronics.
While the high-voltage battery is charged at EV charging stations, the low-voltage battery must be charged onboard from the main battery. This is where the DC/DC converter comes in — stepping down high-voltage DC (400V or higher) to 12V or 24V DC for low-voltage systems.
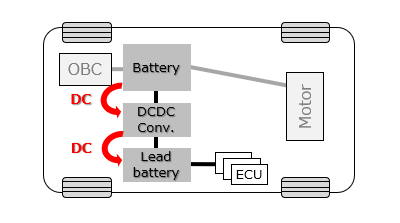
2. What Is a DC/DC Converter in an EV?
A DC/DC converter is an electronic device that converts one DC voltage level to another.
In EVs, it serves a step-down function, ensuring that high-voltage energy from the traction battery is transformed into safe, regulated low-voltage power for vehicle electronics.
3. High Voltage vs. Low Voltage in Electric Vehicles
High-Voltage Applications
* Powers the traction motor and high-load components.
* Maintains efficiency by reducing current, lowering I²R losses, and improving conversion rates.
Low-Voltage Applications
* Powers auxiliary equipment (lights, sensors, infotainment, ECUs).
* Even high-voltage components often have control boards running on low voltage.
* A 12V system remains the global standard due to legacy automotive design.
4. Why EV Low Voltage Is Typically 12V or 24V
* Passenger cars: Six lead-acid cells × 2.1V = ~12.6V nominal.
* Commercial trucks: Two 12V batteries in series for 24V systems to power large starter motors.
This voltage standard simplifies integration with existing automotive electrical architecture.
5. EV DC/DC Converter Market Trends
With EV adoption accelerating, demand for automotive DC/DC converters is projected to rise sharply due to:
* Increased onboard electronics and electrification of auxiliary systems.
* Growing need for high-power, compact, and efficient converters.
* Stricter requirements for high-voltage tolerance, high current capacity, low loss, high heat resistance, and miniaturization.
6. DC/DC Converter Circuit Structure in EVs
Core Functional Blocks:
1, Input Voltage Sensing – Monitors lithium-ion battery voltage.
2, Input Noise Filter – Removes electromagnetic interference (EMI) and voltage spikes.
3, Voltage Conversion Stage – Uses MOSFET switches and isolated transformers for step-down conversion.
4, Output Noise Filter – Ensures stable, ripple-free power.
5, Output Voltage Detection – Maintains precise regulation.
6, Control Circuit – Manages switching and safety logic.
7, Communication Interface – Links to EV control networks (CAN, Ethernet) with ESD protection.
7. Key Design Components for Automotive DC/DC Converters
* Hybrid Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors – For noise suppression and voltage smoothing.
* Automotive Power Inductors – Handle high current with minimal heat loss.
* Chip Varistors – Protect communication lines from static discharge.
* Precision Resistor Networks – For voltage feedback and control accuracy.
8. Conclusion
The DC/DC converter is a critical component in electric vehicles, enabling the safe and efficient operation of all low-voltage systems.
As EV technology advances, the role of the DC/DC converter will expand, driving innovations in power density, efficiency, and thermal management.
Future designs will demand:
* Higher output power capacity
* Better efficiency at high load
* Compact size for integration in space-limited environments


 MCU Solutions
MCU Solutions PCBA Solutions
PCBA Solutions Bluetooth Solutions
Bluetooth Solutions
 FAQ
FAQ Contact Us
Contact Us
 Company News
Company News Technology News
Technology News Industry News
Industry News PCBA News
PCBA News
 Company Profile
Company Profile Certificates
Certificates Terms & Conditions
Terms & Conditions Privacy Statement
Privacy Statement
 Home Appliances
Home Appliances Beauty Appliances
Beauty Appliances Lighting
Lighting Kid's Toys
Kid's Toys Security Alarm
Security Alarm Health Care
Health Care



 More information?
More information?






